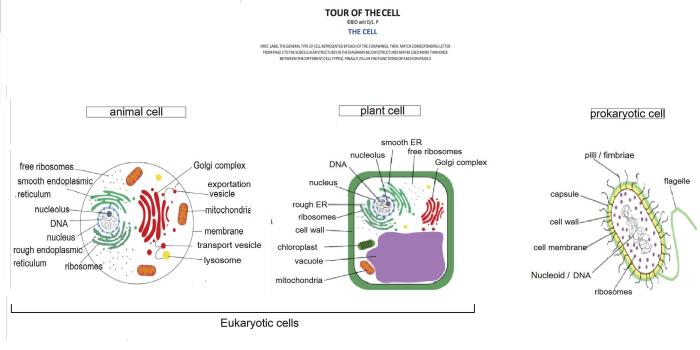
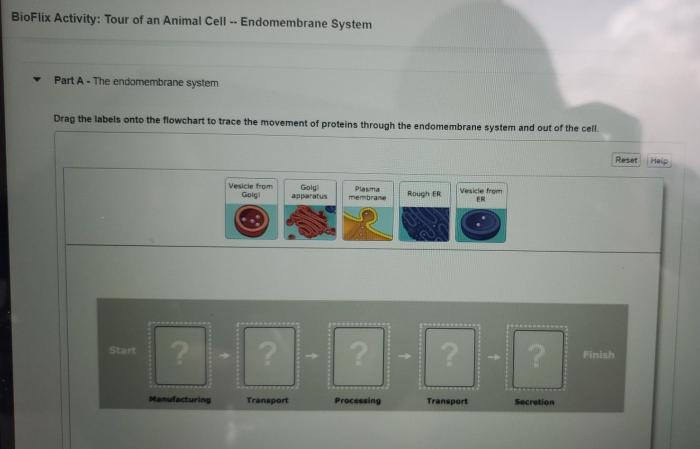
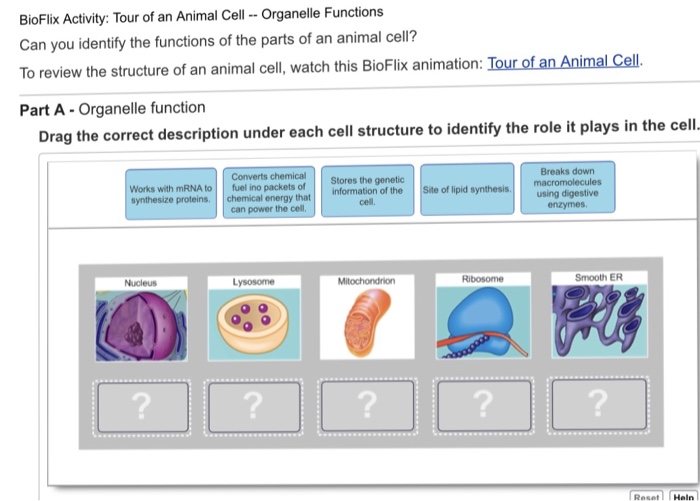
Bioflix activity: tour of a plant cell — cell structures unveils the intricate inner workings of plant cells, inviting readers to embark on a captivating journey of discovery.
This interactive experience provides an immersive exploration of the essential organelles and structures that orchestrate the life processes within plant cells, fostering a deep understanding of their functions and significance.
Introduction: Bioflix Activity: Tour Of A Plant Cell — Cell Structures
Understanding the structures of plant cells is essential for comprehending the fundamental processes that sustain life on Earth. By visualizing these structures, we can gain insights into their specific functions and roles in maintaining cell viability.
Interactive Tour of a Plant Cell
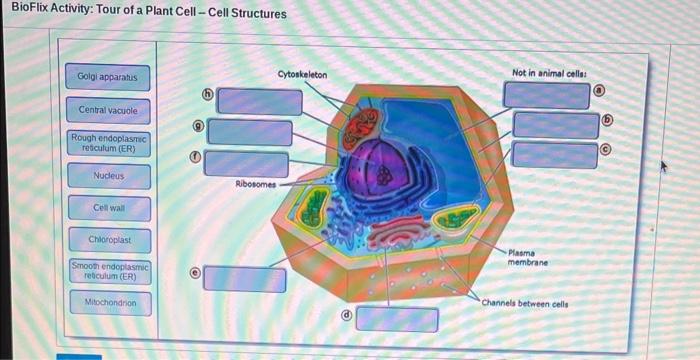
To facilitate an immersive learning experience, we propose an interactive tour of a plant cell. This virtual environment will allow users to explore and engage with various organelles and structures, gaining a comprehensive understanding of their functions.
Key Structures and Functions
- Cell Wall:Provides structural support and protection.
- Cell Membrane:Regulates cell entry and exit, maintaining cellular integrity.
- Nucleus:Houses genetic material and controls cell activities.
- Ribosomes:Synthesize proteins essential for cellular functions.
- Chloroplasts:Capture sunlight and convert it into energy through photosynthesis.
- Mitochondria:Generate energy for cellular processes.
- Vacuoles:Store water, nutrients, and waste products.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum:Synthesizes and transports proteins and lipids.
- Golgi Apparatus:Modifies and packages proteins and lipids for secretion.
- Lysosomes:Contain digestive enzymes to break down cellular waste.
- Cytoskeleton:Provides structural support and facilitates cell movement.
Cell Wall and Membrane, Bioflix activity: tour of a plant cell — cell structures
The plant cell wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, providing rigidity and protection. The cell membrane, composed of a phospholipid bilayer, regulates the entry and exit of molecules, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Nucleus and Ribosomes
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material (DNA). Ribosomes, composed of RNA and protein, are responsible for protein synthesis.
Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight and converts it into energy through photosynthesis. Mitochondria generate energy through cellular respiration, using oxygen to break down glucose.
Vacuoles and Endoplasmic Reticulum
Vacuoles are membrane-bound compartments that store water, nutrients, and waste products. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that synthesizes and transports proteins and lipids.
Golgi Apparatus and Lysosomes
The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins and lipids for secretion. Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes to break down cellular waste.
Cytoskeleton and Cell Division
The cytoskeleton, composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, provides structural support and facilitates cell movement. Cell division is the process by which cells divide to create new cells, ensuring growth and tissue repair.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of understanding plant cell structures?
Comprehending plant cell structures is crucial for unraveling the fundamental processes that govern plant growth, development, and response to environmental cues.
How does visualizing these structures enhance learning?
Visualization through interactive tours provides a tangible and engaging experience, enabling learners to grasp complex concepts more effectively and retain information more efficiently.
What are the key structures and functions within a plant cell?
Essential structures include the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, ribosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes, each playing specific roles in maintaining cell viability and function.